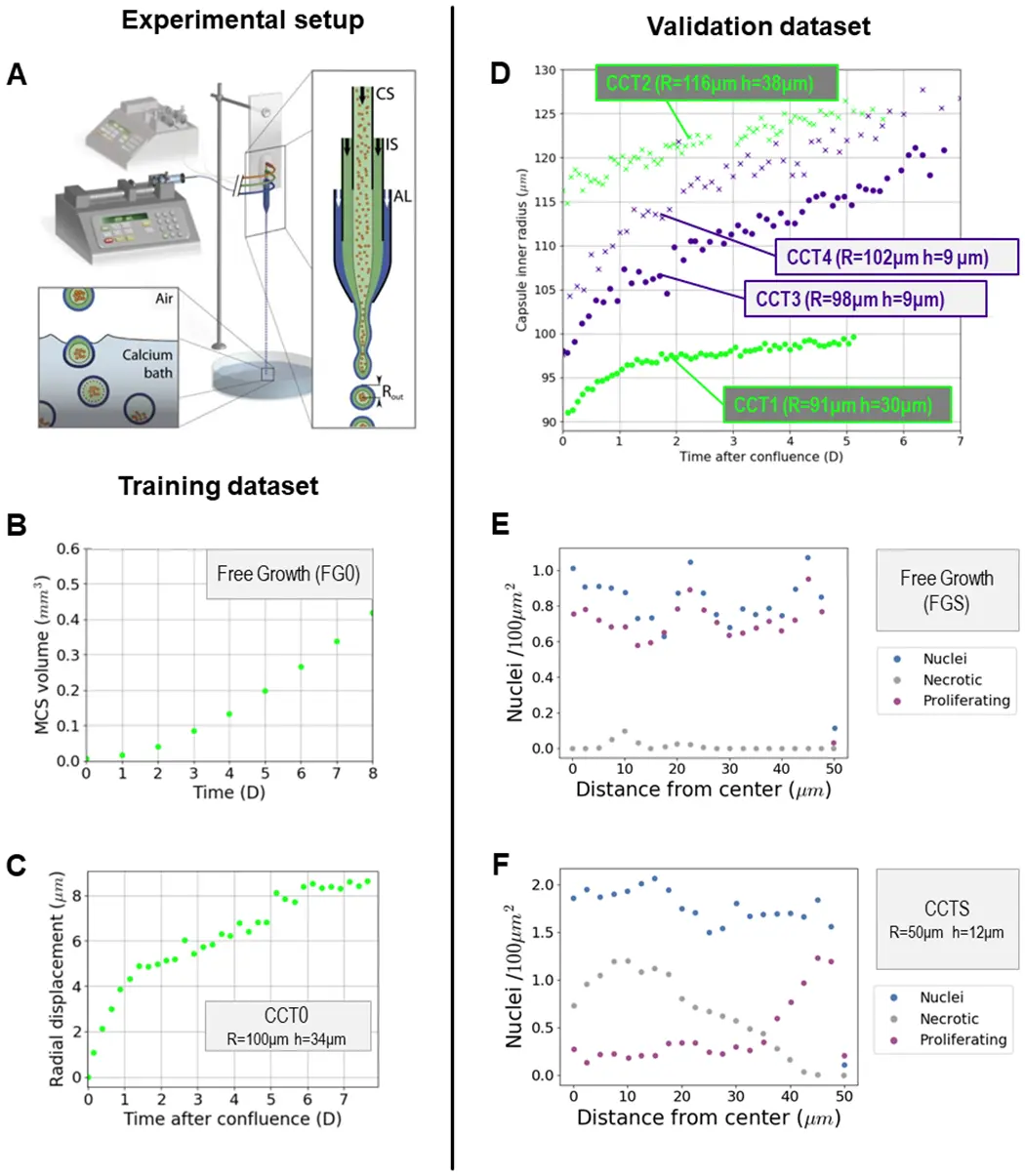
Overview of Cellular Capsules Technology (CCT)
Cellular Capsules Technology (CCT) is an innovative method that involves encapsulating cells within tiny, semi-permeable hydrogel capsules. These capsules provide a protective and controlled microenvironment where cells can proliferate and organize into 3D structures. The capsules allow the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and signaling molecules while isolating the cells from external mechanical stresses. This approach offers a unique way to culture tumor cells in a more natural state, preserving their heterogeneity and functionality during the organoid formation process.
Digital twinning of Cellular Capsule Technology: Emerging outcomes from the perspective of porous media mechanics
Advantages of Using CCT for Tumor Organoid Production
Using CCT to generate tumor organoids presents several key advantages. First, the semi-permeable capsules improve nutrient and oxygen diffusion, which is often a limiting factor in 3D cultures. This ensures healthier, more viable organoids that better replicate in vivo conditions. Second, CCT provides a reproducible and scalable platform, enabling consistent production of uniform organoids suitable for high-throughput drug screening. Third, the capsules protect delicate cell aggregates from shear stress during handling and expansion, maintaining tumor heterogeneity critical for studying different cancer subtypes and treatment responses.
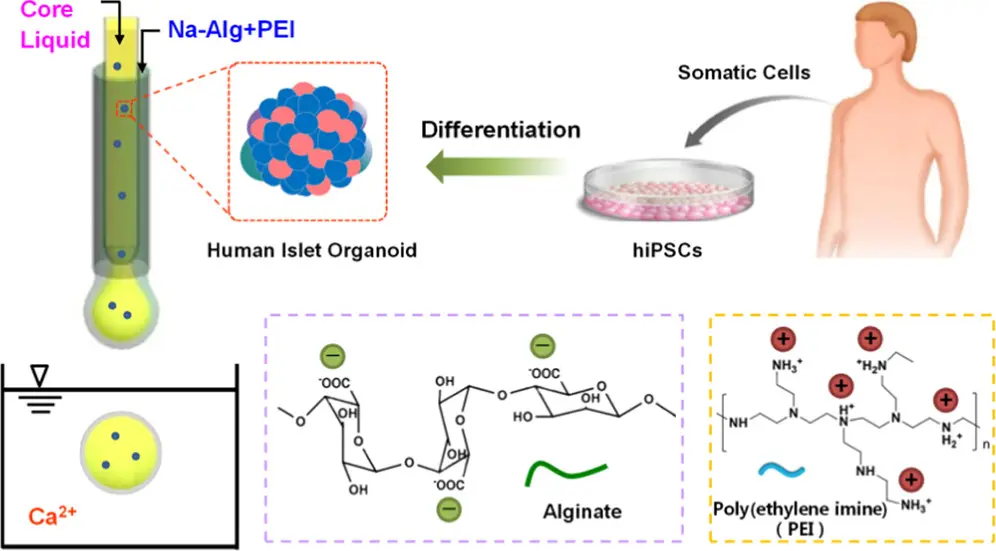
Fabrication process and the formation mechanism of Alg/PEI macrocapsules for encapsulation of human islet organoids
Applications in Cancer Research and Drug Testing
3D tumor organoids created with CCT have wide-ranging applications in cancer research. They serve as powerful tools for personalized medicine by allowing the growth of patient-derived tumor cells, facilitating tailored drug sensitivity testing. This technology also accelerates drug discovery by providing a more predictive model for screening anti-cancer compounds, reducing reliance on animal models. Furthermore, CCT-based organoids help researchers investigate tumor biology, including mechanisms of drug resistance, invasion, and interaction with the tumor microenvironment, ultimately contributing to improved therapeutic strategies.
Comparison with Other 3D Culture Methods
While several 3D culture methods exist including spheroids, hydrogel matrices, and bioprinting CCT offers distinct advantages. Unlike spheroids, which can suffer from inconsistent size and necrotic cores due to poor nutrient diffusion, CCT capsules ensure better mass transport, resulting in healthier organoids. Compared to hydrogels, which can have variable mechanical properties and may interfere with cell signaling, the capsules provide a more controlled and tunable environment. Additionally, CCT enables easier handling and scalability compared to complex bioprinting techniques, making it attractive for routine lab and industrial applications.
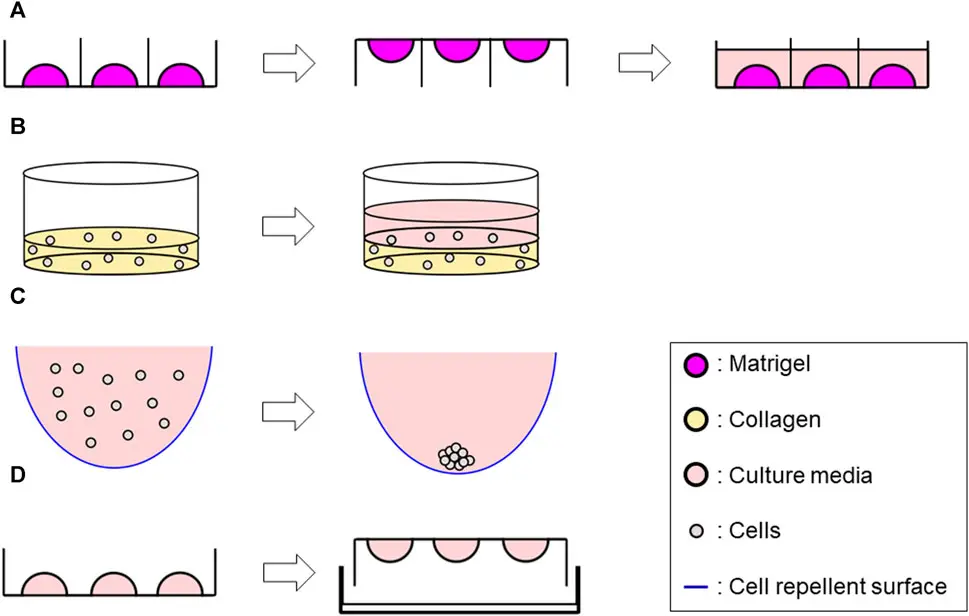 Comparison of three-dimensional cell culture techniques of dedifferentiated liposarcoma and their integration with future research
Comparison of three-dimensional cell culture techniques of dedifferentiated liposarcoma and their integration with future research
Conclusion
Cellular Capsules Technology offers a groundbreaking platform for generating 3D tumor organoids that faithfully replicate the complex biology of human tumors. By enhancing nutrient diffusion, protecting cell integrity, and enabling scalable production, CCT advances cancer modeling beyond traditional methods. This technology holds great promise for accelerating drug discovery, enabling personalized treatment strategies, and deepening our understanding of tumor behavior. As research and development continue, CCT-based tumor organoids are likely to become essential tools in the fight against cancer.